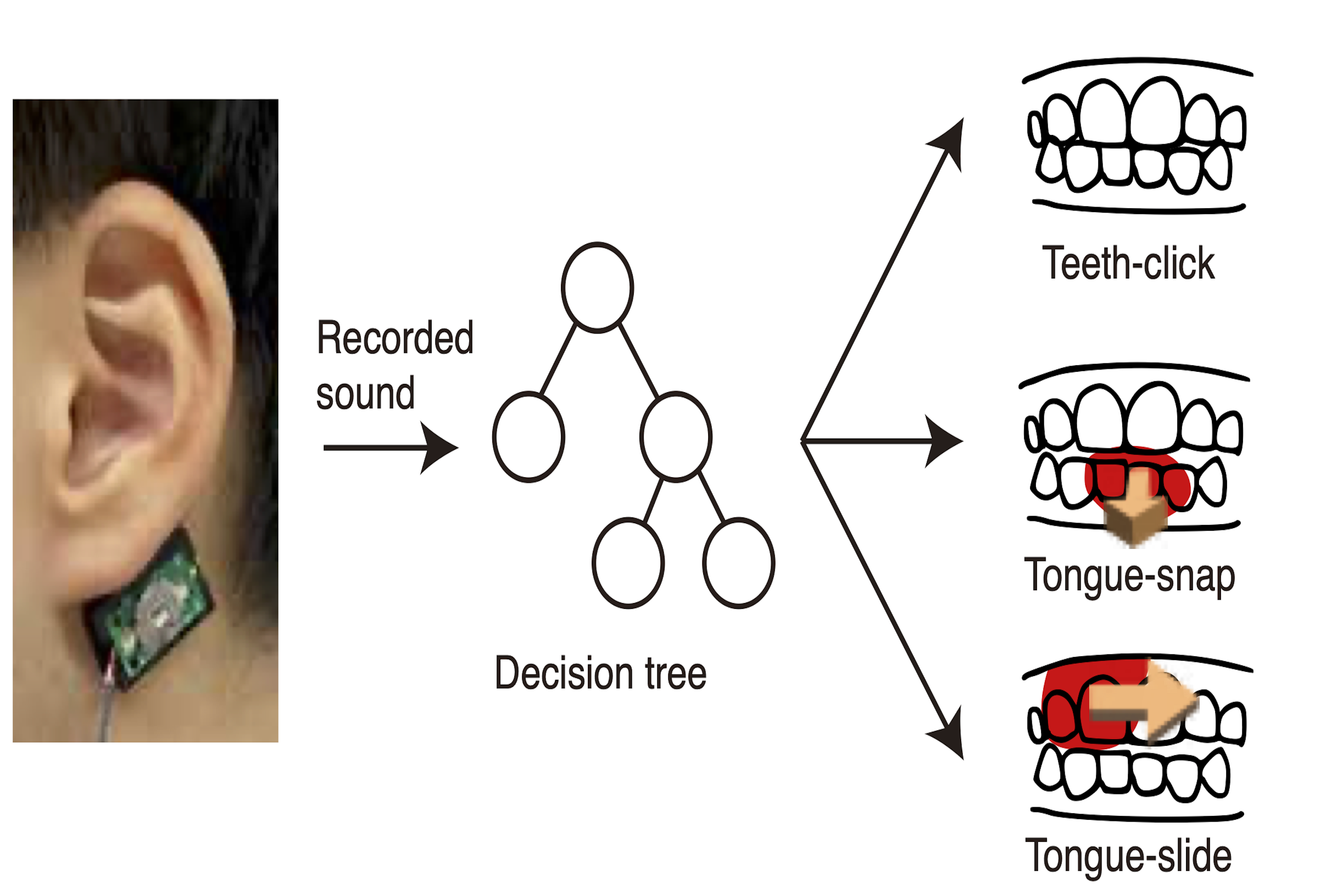
ウェアラブルデバイスに対するハンズフリーかつ周囲に気づかれない入力手法として舌を用いたジェスチャが研究されている。しかし舌の動きは微かなものであるため、口周りにセンサを設置する必要があり、装着感や目立ちやすさに課題がある。そこで本研究では舌で歯を弾いたり擦ったりすることで生じる音を利用し、耳の後ろに設置した骨伝導マイクによって舌の動きを認識することを提案する。そして音のスペクトルを入力とし、決定木による舌や歯の動かし方の種類の識別を行った。
Tongue gestures have been studied as a hands-free and unnoticeable input method for wearable devices. However, tongue movements are slight, requiring the placement of sensors around the mouth, causing wearability issues and conspicuousness. We propose recognizing tongue movements using the sound produced by tapping or snapping the tongue against the teeth, detected by a bone conduction microphone placed behind the ear. A decision tree using the spectrum of bone-conduction sounds classified three different gestures: clicking the teeth, snapping the tongue, and sliding the tongue against the teeth.
Shogo Tomaru, Ken Takaki, Hiroaki Murakami, Koya Narumi, Mitsuhiro Kamezaki, Yoshihiro Kawahara
関連論文/Related Publications
S.Tomaru, K.Takaki, H.Murakami, D.Kim, K.Narumi, M.Kamezaki, and Y.Kawahara, “Micro-Gesture Recognition of Tongue via Bone Conduction Sound,” Adjunct Proc. of ACM UIST 2024, Article No. 96, pp. 1-3, Pittsburgh, US, Oct. 2024.
連絡先/Contact
tomaru@akg.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp